Using solar energy to generate heat at high temperatures
Instead of burning coal or oil to produce cement or steel, in the future solar energy could be used for this purpose. Researchers at ETH Zurich have developed a thermal trap that can absorb concentrated sunlight and deliver heat at over thousand degrees Celsius.
In brief
- A new thermal trap developed by researchers at ETH Zurich uses sunlight to reach a temperature of over thousand degrees Celsius.
- The new technology minimises heat losses and thus makes it possible to generate this high temperature efficiently
- The approach could help to provide industrial plants with high temperatures and thus make these industries carbon neutral.
The production of cement, metals and many chemical commodities requires extremely high temperatures of over a thousand degrees Celsius. At present, this heat is usually obtained by combusting fossil fuels: coal or natural gas, which emit large amounts of greenhouse gases. Heating with renewable electricity is not an alternative, as this would be inefficient at these high temperatures. Although much of our economy and society will need to become carbon neutral in the coming decades, these industrial processes are likely to continue to be powered by fossil fuels for the near future. They are considered difficult to decarbonise.
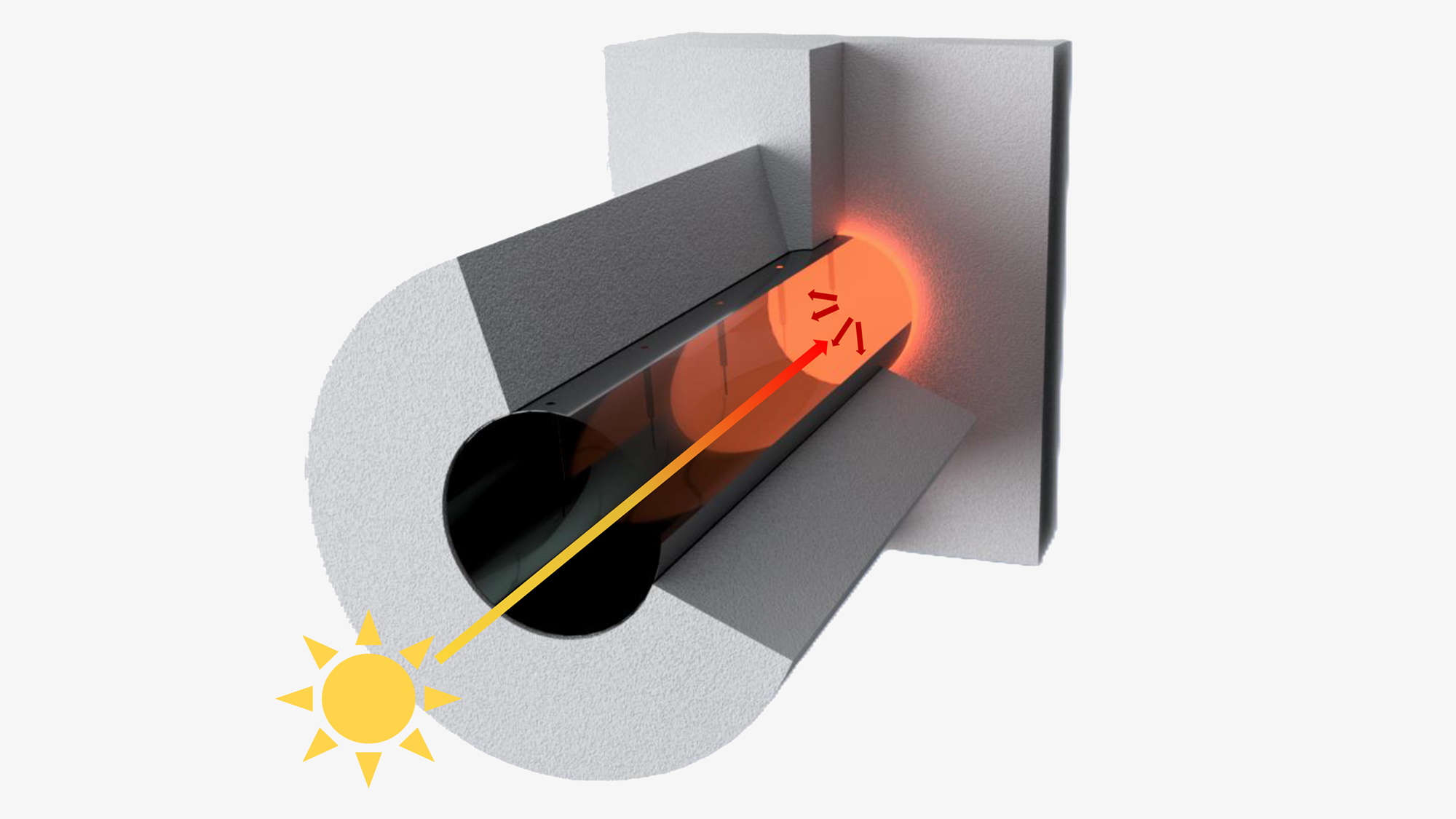
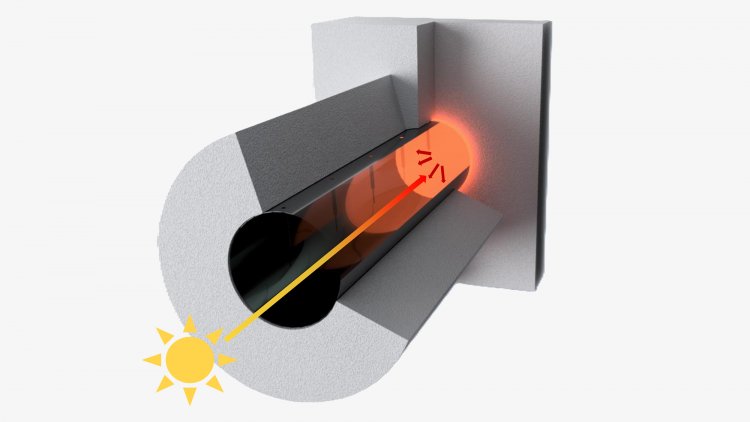
Researchers at ETH Zurich have now demonstrated, in the lab, a way to make these industries independent of fossil fuels. Using solar radiation, they have engineered a device that can deliver heat at the high temperatures needed for the production processes. The team led by Emiliano Casati, a scientist in the Energy and Process Systems Engineering Group, and Aldo Steinfeld, Professor of Renewable Energy Carriers, has developed a thermal trap. It consists of a quartz rod coupled to a ceramic absorber which, thanks to its optical properties, can efficiently absorb sunlight and convert it into heat.
In their lab-scale experiments, the team used a quartz rod measuring 7.5 centimetres in diameter and 30 centimetres in length. They exposed it to artificial light with an intensity equivalent to 135 times that of sunlight, reaching temperatures of up to 1050 degrees Celsius. Previous studies by other researchers have achieved a maximum of 170 degrees with such thermal traps.