Taste Buds
Taste buds are tiny sensory organs that allow you to experience taste. They’re located inside the tiny bumps covering your tongue called papillae. Taste buds let you know what you’re eating and drinking and whether it tastes “good” or “bad.” This information makes eating pleasurable, which helps keep your body nourished. Your taste buds also alert you when something isn’t safe to consume, like spoiled milk or rotten meat.
What are taste buds?
Taste buds are tiny sensory organs that allow you to experience taste. They’re located inside the tiny bumps covering your tongue called papillae. Taste buds let you know what you’re eating and drinking and whether it tastes “good” or “bad.” This information makes eating pleasurable, which helps keep your body nourished. Your taste buds also alert you when something isn’t safe to consume, like spoiled milk or rotten meat.
Overview

What are taste buds?
Taste buds are tiny sensory organs that allow you to experience taste. They’re located inside the tiny bumps covering your tongue called papillae. Taste buds let you know what you’re eating and drinking and whether it tastes “good” or “bad.” This information makes eating pleasurable, which helps keep your body nourished. Your taste buds also alert you when something isn’t safe to consume, like spoiled milk or rotten meat.
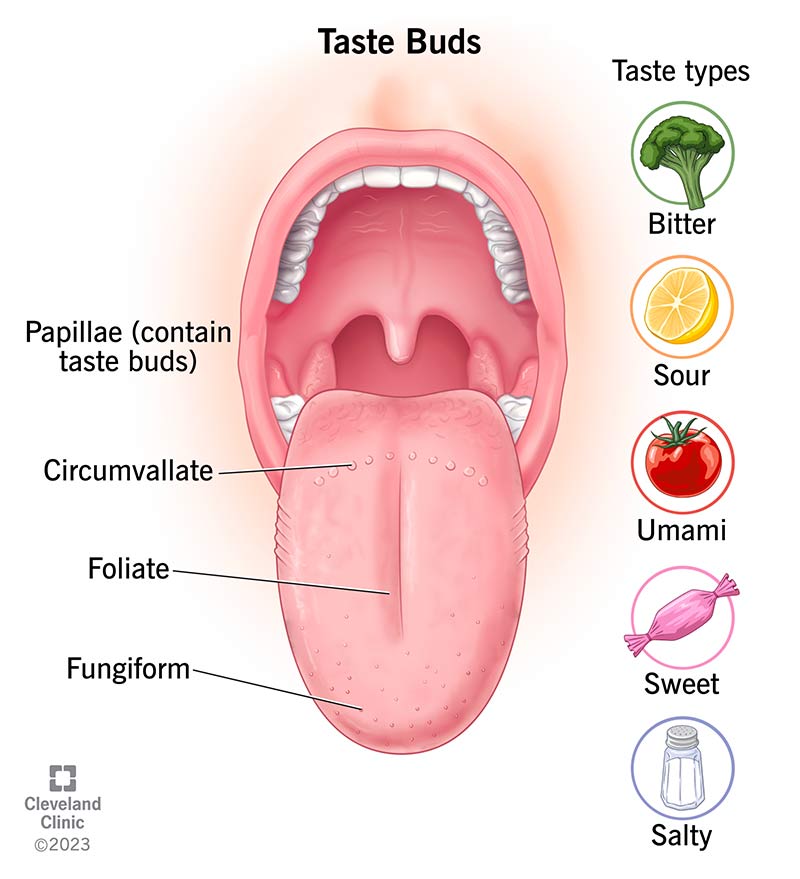
What tastes can taste buds detect?
Taste buds detect five basic tastes, including:
- Sweet: Sweet foods mostly contain some form of sugar (sucrose, glucose, fructose and lactose). They include foods like honey, fruit and ice cream.
- Salty: Salty foods contain table salt (sodium chloride) or mineral salts, like magnesium or potassium. Think of foods like pretzels, chips and movie theater popcorn.
- Bitter: Bitter foods may contain ingredients like caffeine or compounds from plants, among others. Bitter is a complex taste regarding whether your taste buds recognize it as “good” or “bad.” For example, some people like bitter foods, like coffee and dark chocolate, while others don’t.
- Sour: Sour foods, like citrus fruits and vinegar, often contain some form of acid (acetic acid, citric acid, lactic acid).
- Umami: Umami is a savory, rich or meaty flavor. Many foods that your taste buds register as umami contain a substance called glutamate. Umami foods include tomatoes, asparagus, fish, mushrooms and soy.
Your taste buds experience these tastes in various combinations, making your experience of food and drink all the more complex. For example, taste buds may register a food as mostly sweet but also salty and umami. Or, a drink may taste mostly bitter but also sweet.























